Buddy Allocator
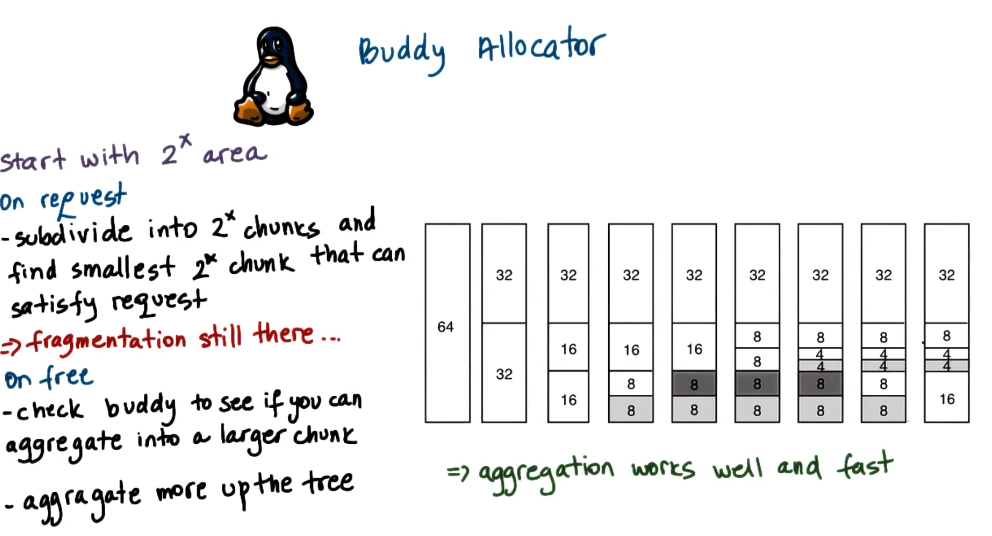
The buddy allocator is a memory allocator used in the linux kernel to efficiently manage contiguous blocks of memory. It works by dividing memory into blocks of sizes that are powers of 2.
How It Works
- Allocation:
- Memory is initially available as large power-of-2 blocks.
- When a request is made, the allocator finds the smallest block that fits the request.
- If the block is too large, it recursively splits it into two equal “buddies” until the requested size is reached.
- Deallocation & Merging (“Buddy System”)
- When memory is freed, the allocator checks whether its buddy (the adjacent block of the same size) is also free.
- If both buddies are free, they are merged back into a larger block.
- This process continues up the hierarchy, helping to reduce fragmentation.
Advantages & Trade-offs
Fast allocation & deallocation: Simple bitwise operations track buddy pairs.
Merging reduces fragmentation: Helps prevent external fragmentation.
Internal fragmentation → Requests that don’t match a power-of-2 size may waste memory.