ARTEMIS
ARTEMIS is a system designed to detect and mitigate BGP Hijacking, operated locally by network operators to protect their own prefixes. The system is based on several key ideas and can be found in this paper.
This works in the following way.
- Write a configuration File: Lists all prefixes owned by the network, created by the network operator.
- BGP Updates Mechanism: Receives updates from local routers and monitoring services.
- Anomaly Detection: Compares received BGP updates against the configuration file to detect anomalies in prefixes and AS-PATH fields.
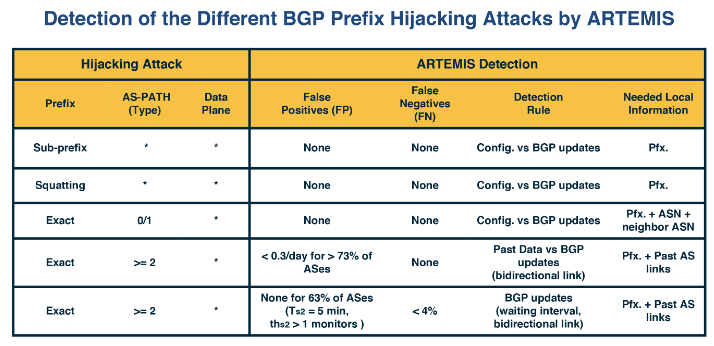
ARTEMIS can detect different types of BGP prefix hijacking attacks by monitoring for unusual patterns in BGP announcements.
The system aims to minimise false positives and false negatives. Operators can prioritise between accuracy and speed or opt for fewer inconsequential FNs at the cost of higher FPs.
This is achieved by
- Prefix Deaggregation: The affected network announces more specific prefixes to counteract hijacked prefixes. For example, if a prefix 208.65.153.0/24 is hijacked, the network could announce 208.65.153.128/25 and 208.65.153.0/25.
- Multiple Origin AS (MOAS): Third-party organisations announce the hijacked prefixes from their locations. This attracts global traffic to the third party, which scrubs it and tunnels it back to the legitimate AS.