Week 5 - Beyond Multiprocessing … Multithreading and the SunOS Kernel
Ref: Beyond Multiprocessing … Multithreading the SunOS Kernel
Notes
Architecture
In this paper they introduce the concept of a Light Weight Process (LWP) that sits as an intermediary between kernel level threads and user level threads. Each LWP is mapped to a kernel thread but not all kernel threads need to be mapped to a LWP.
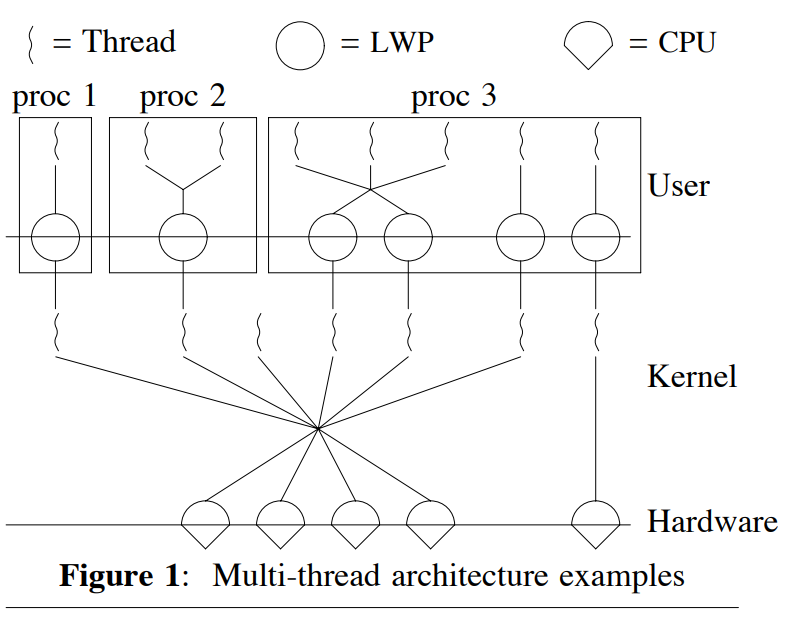
The threading library controls the mappings between user level threads and light weight processes. This separation allows for the threading library to switch user level thread without needing to make a system call. It also allows for massive amounts of user level threads without overwhelming the kernels resources.
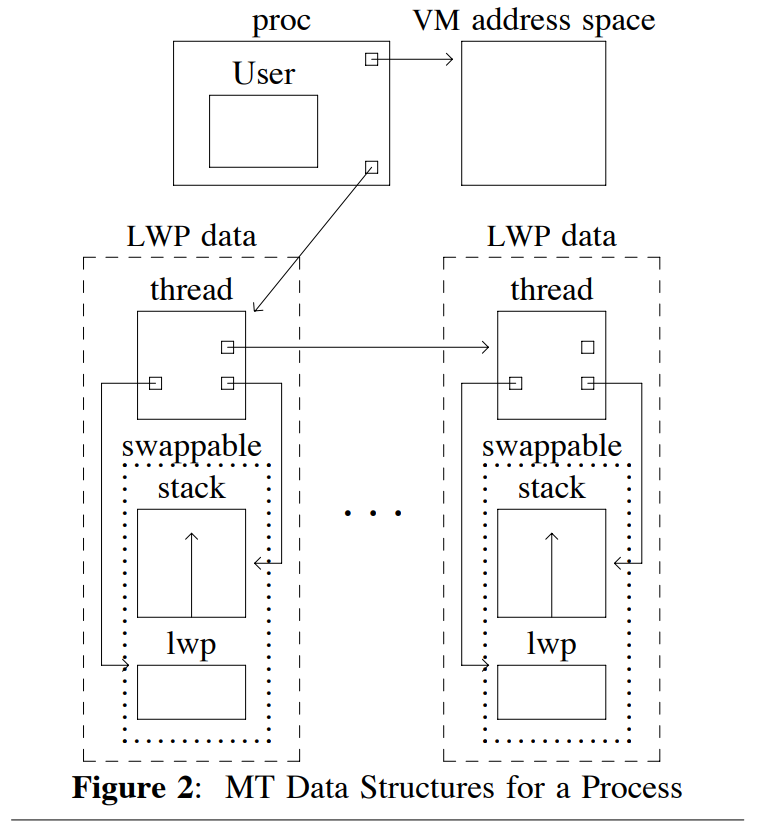
In figure 2 you see how they have separated up the data that is needed for the PCB into small subblocks. The components within the LWP are swappable for different user level threads, meaning when a context switch is required in the LWP there is less overhead in that.
The proc data structure contains:
- list of kernel threads associated with the process,
- a pointer to the process address space,
- user credentials, and
- the list of signal handlers.
The kernel thread structure contains:
- kernel registers,
- scheduling class,
- dispatch queue links, and
- pointers to:
- the stack,
- associated LWP,
- processs, and
- CPU structure.
The LWP data structure contains:
- the PCB for storing user-level registers,
- system call arguments,
- signal handling masks,
- resource usage information,
- profiling pointers, and
- pointers to:
- the associated kernel thread, and
- process structures.
Scheduling
SunOS uses real time scheduling. On each CPU the highest priority kernal thread gets scheduled. Simultaneously the highest priority user thread gets scheduled on that LWP. If joint it uses round robin.
SunOS implements preemptive threads. This means as soon as a higher priority thread becomes runable it is scheduled immediately to be running on a CPU. This can cause strange reordering of threads where an event causing a change of executing thread may happen on another CPU which then effects the running thread on another CPU.